Form Factor
For homogeneous objects, the form factor is expressed as
For a sphere of radius the formula above evaluates to
Fig. 1 shows the form factor of a sphere according to the formula above. In agreement with what stated in the previous paragraph, we notice that for the form factor attains a plateau at a value of 1, whereas as soon as qR becomes substantially larger than 1 the form factor is affected by the interparticle interference effects.
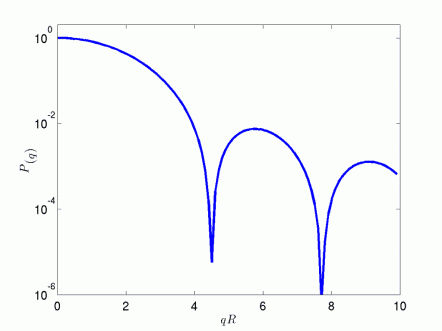
Figure 1: Sphere Form Factor.
A simpler general formula for the form factor can be obtained by introducing the so-called pair distance function, g(r) i.e. the probability to find two points belonging to the colloidal particle at a distance :
By expanding in series the term we obtain the Guinier approximation for the form factor:
where the (optical) radius of gyration is defined as
The importance of such approximation lies in the fact that it allows for the determination of a size parameter, namely by performing a simple linear fit in the plot
vs.
, the so-called Guinier plot. As an example, Fig. 3 shows the approximation for a sphere for which
.
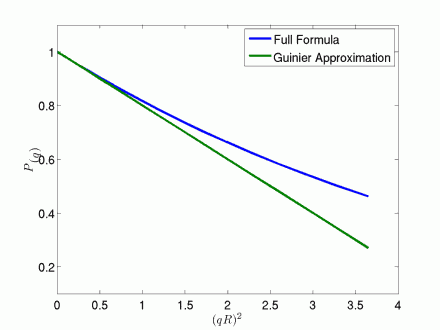
Figure 2: Sphere Form Factor, Guinier Plot.
